Press release -
The Swedish Energy Agency grants support for establishing a carbon dioxide infrastructure in southern Sweden
Malmö CO2 Hub, a collaboration between several industrial and energy companies in southern Sweden, has been granted SEK 5.3 million in financial support from the Swedish Energy Agency (Energimyndigheten), within the framework of the Industriklivet - The Industrial Leap funding. The purpose of the project is to develop a common infrastructure in the region for transport and storage or utilisation of carbon dioxide (CCUS).
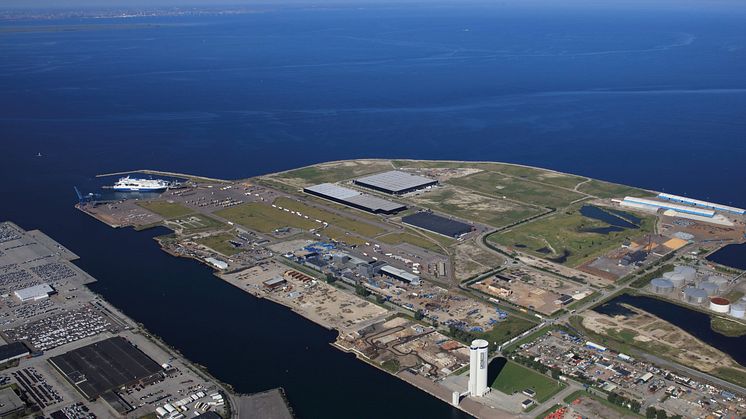
Malmö CO2 Hub is a joint project between several parties active in energy, port logistics and waste management sectors: Copenhagen Malmö Port, E.ON, Nordion Energi, Sysav and Uniper, with the support of Växjö Energi and Öresundskraft. The financial support from the Swedish Energy Agency will be used to develop an in-depth feasibility study for a common carbon infrastructure in southern Sweden, including transportation and final geological storage. The feasibility study will be completed in June 2025.
Collaboration that lowers costs and opens up for more participants
A common system for the transport and storage or utilisation of carbon dioxide would allow companies in the carbon dioxide hub to share investment costs, making Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage more financially accessible and thus increasing the reductions emission of reductions. The goal is to develop a sustainable CCUS infrastructure that is open to additional stakeholders.
“By collaborating on a carbon capture, utilisation and storage infrastructure, we can achieve climate benefits not only for industry but also for Sweden as a whole,” comments Project Manager Henrik Norgren. “The project provides economies of scale and reduced costs for all participating companies, making it easier for us to contribute to achieving Sweden’s climate goals. This funding from the Swedish Energy Agency and our partners makes this possible, and establishes a model that other Regions can derive inspiration from.”
A solution for sustainable industrial development and climate change
Carbon capture has been identified as an important component in achieving the climate targets set by Sweden and the EU to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The thinking behind the project is to establish Malmö as a carbon dioxide logistics hub, where carbon dioxide can be collected and transported for final storage, in Norway or Denmark for example. Together, the parties involved in Malmö CO2Hub are working to build out an infrastructure that enables 1-2 million tonnes of carbon dioxide to be captured and stored annually. This would thus contribute to achieving negative emissions and a more sustainable industrial production in Sweden.
Facts in brief: CCUS – Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage
CCUS refers to Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage, technology that captures carbon dioxide emissions from industrial facilities and power plants. The objective is to prevent CO2from being released into the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. The process involves three main steps: capture, transport and storage (or utilisation) of the carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is captured either directly at the source of the emissions or from the atmosphere. After the capture, it will be transported to a storage site, often an intermediate storage facility, for further transport later. The final destination for storage is usually underground geological formations, such as depleted oil or gas fields. Carbon dioxide can also be utilised: either as a raw material in the products of fuels or as new raw material. CCUS is an increasingly important technology for achieving climate action goals, especially in sectors where emissions reduction is challenging.
Facts in brief: CNetSS – Carbon Network South Sweden
Malmö CO₂ Hub is an advancement of the CNETSS collaboration. CNetSS has the long-term goal of increasing the potential for reducing emissions and achieving “negative emissions.” Participants in phases 1 and 2 were SYSAV (South Scania Waste), CMP (Copenhagen Malmö Port), E.ON, Växjö Energi, Öresundskraft, Nordion Energi, Kraftringen, Höganäs, Kemira and Stora Enso. These phases resulted in the port in Malmö being identified as the most suitable location for an intermediate storage facility for carbon dioxide. The project has determined the amount and timing of the quantities of carbon dioxide to be captured by the participants, the most appropriate methods for transport to the intermediate storage facility, as well as the size of the storage facility and the physical storage requirements of the intermediate storage facility. The project is being conducted with the financial and other support from Industriklivet - The Industrial Leap.
Phase 3 is project managed by Nordion Energi, and the goal here is to define in greater detail the business model, technology, costs and legal aspects, prior to the procurement of a system solution.
Facts in brief: Industriklivet – The Industrial Leap
Industriklivet - The Industrial Leap is a governmental initiative to support the green transition by providing funding for innovative projects which will benefit the environment. Within the project, the Swedish Energy Agency can award grants for feasibility and pilot studies, research projects, pilot projects and demonstration projects, along with investments in various areas.
Industriklivet will cover SEK 1,457 million of the costs in 2024 and can finance projects that will continue until 2031.